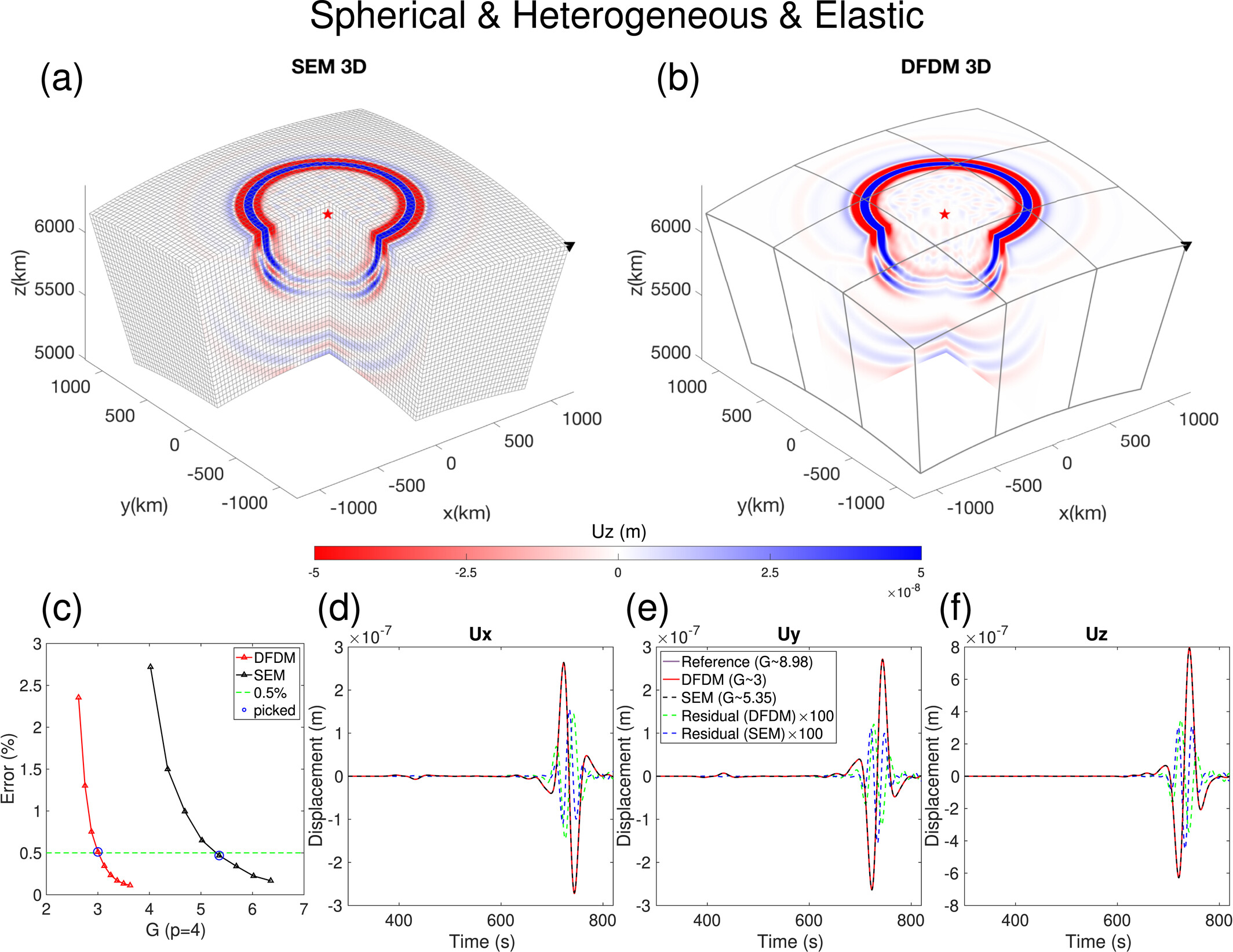
Instrumenting the Ocean Floor
This is a collaborative project between the Berkeley Seismological Laboratory (BSL) and the Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute (MBARI)
An Underwater Observatory
This is a collaborative project between the Berkeley Seismological Laboratory (BSL) and the Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute (MBARI). PI’s are Barbara Romanowicz at UC Berkeley and Paul McGill at MBARI. A three-component very broadband seismometer package (CMG-1T), recording system, as well as an auxiliary differential pressure gauge (DPG) and current meter, were installed on the seafloor, in Monterey Bay, 40 km off-shore, at 1000m water depth, in April of 2002.
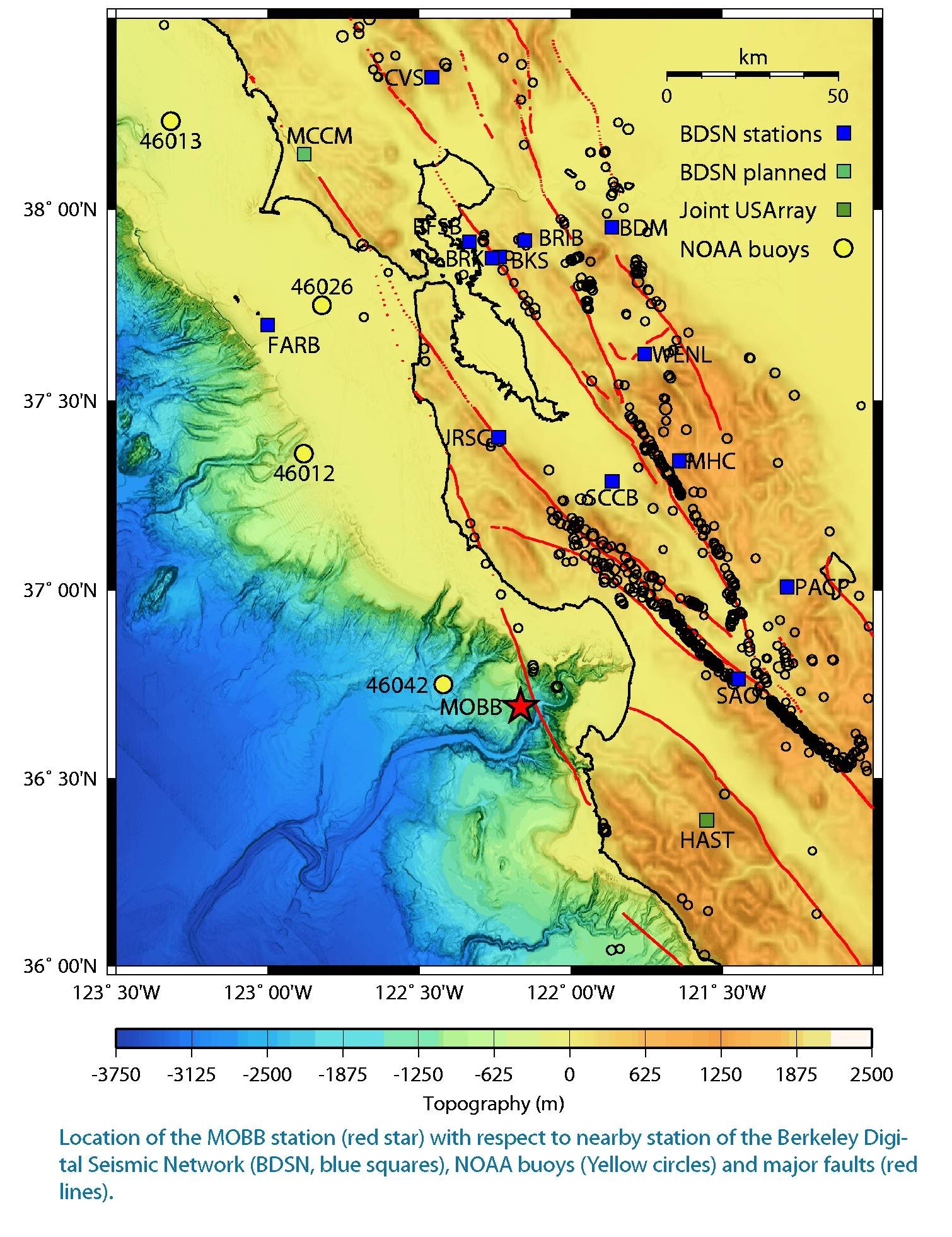 Figure 1: Map showing the location of the MOBB observatory in Monterey Bay.
Figure 1: Map showing the location of the MOBB observatory in Monterey Bay.
The seismic package was installed in a PVC pipe using the MBARI ROV Ventana and is buried under the seafloor, covered with glass beads. The recording system and battery package sits 10m away in an anti-trawling device, whose design served as a prototype for the housing of the MARS cable junctions (click here). The MOBB observatory is currently autonomous: data cartridges and batteries are exchanged every 4 months using dives of the ROV Ventana from the MBARI ship Point Lobos.
We are currently working on hardware and software to connect the observatory to the MARS cable. Once connected, the data from MOBB will be combined in real-time with the data from the land-based broadband network in northern California.
For more information on the project, visit the MOBB page at MBARI.
See related papers:
- Romanowicz, B., D. Stakes, R. Uhrhammer, P. McGill, D. Neuhauser, T. Ramirez, D. Dolenc (2003) “The MOBB experiment: a prototype permanent off-shore ocean bottom broadband station,” EOS Trans AGU, 84, 325-332.
- Romanowicz, B., D. Stakes, D. Dolenc, P. McGill, R. Uhrhammer, and T. Ramirez (2006) “The Monterey Bay Broadband Ocean Bottom Seismic Observatory,” Annals of Geophysics.
Publications Related to MOBB Data Analysis
The MOBB data have been used for a variety of purposes. Two sources of background noise are particularly problematic in ocean bottom broadband seismic deployments:
- Long period noise in the infragravity wave band.
- Signal-generated noise due to reverberations in the sediment column.
Related Research Papers:
-
Dolenc, D., B. Romanowicz, R. Uhrhammer, P. McGill, D. Neuhauser, and D. Stakes (2006) “Identifying and Removing Noise from the Monterey Ocean Bottom Broadband Seismic Station (MOBB) data,” G-Cubed, 8, doi:10.1029/2006GC001403. See also BSL Annual report for more detailed information.
-
Dolenc, D., B. Romanowicz, D. Stakes, P. McGill, and D. Neuhauser (2005) “Observations of infragravity waves at the Monterey Ocean Bottom broadband station (MOBB),” Geochem, Geophys. Geosyst., 5, Q09002, doi:10.1029/2005GC000988.

Figure 2: Connections to the MOBB observatory showing the junction and deployment setup.

Figure 3: Deployment of the MOBB observatory using ROV Ventana.
The MOISE Experiment
The MOISE project followed a 3-month deployment in 1998 of a “half-buried” broadband seismic package in a similar location in Monterey Bay. This temporary deployment, MOISE (MOnterey Ocean bottom International Seismic Experiment), was a collaboration between MBARI, the Institut de Physique du Globe in Paris (IPGP), the Universite de Bretagne Occidentale (UBO), and the Berkeley Seismological Laboratory.
The seismic package and recording system were installed with the help of the ROV Ventana and featured the first underwater connections performed from the ship Point Lobos between the seismometer package, and recording and battery packages.
See Related Papers:
- Stakes, D., B. Romanowicz, J.P. Montagner, P. Tarits, J-F. Karczewski, S. Etchemendy, D. Neuhauser, P. McGill, J.C. Koenig, J. Savary, M. Begnaud, M. Pasyanos (1998) “MOISE: Monterey Bay Ocean Bottom International Seismic Experiment,” EOS Trans AGU, 79, 301-309.
- Romanowicz, B., D. Stakes, J.P. Montagner, P. Tarits, R. Uhrhammer, M. Begnaud, E. Stutzmann, M. Pasyanos, J-F. Karczewski, S. Etchemendy, D. Neuhauser (1998) “MOISE: A pilot experiment towards long-term sea-floor observatories,” Earth, Planets and Space, 50, 927-937.
For more information about MOISE and the data produced, visit MOISE at MBARI.